Render Volume
In this tutorial, you will learn how to render a volume.
Preface
In order to render a volume we need:
- HTMLDivElements to render different orientation of the volume (e.g., one for Axial, one for Sagittal)
- The path to the images (
imageIds).
Implementation
We have already stored images on a server for the purpose of this tutorial.
First let's create two HTMLDivElements and style them to contain viewports.
const content = document.getElementById('content');
const viewportGrid = document.createElement('div');
viewportGrid.style.display = 'flex';
viewportGrid.style.flexDirection = 'row';
// element for axial view
const element1 = document.createElement('div');
element1.style.width = '500px';
element1.style.height = '500px';
// element for sagittal view
const element2 = document.createElement('div');
element2.style.width = '500px';
element2.style.height = '500px';
viewportGrid.appendChild(element1);
viewportGrid.appendChild(element2);
content.appendChild(viewportGrid);
Next, we need a renderingEngine
const renderingEngineId = 'myRenderingEngine';
const renderingEngine = new RenderingEngine(renderingEngineId);
Loading a volume is possible by using the volumeLoader API.
// note we need to add the cornerstoneStreamingImageVolume: to
// use the streaming volume loader
const volumeId = 'cornerStreamingImageVolume: myVolume';
// Define a volume in memory
const volume = await volumeLoader.createAndCacheVolume(volumeId, { imageIds });
We can then create a viewports inside the renderingEngine by using the setViewports API.
const viewportId1 = 'CT_AXIAL';
const viewportId2 = 'CT_SAGITTAL';
const viewportInput = [
{
viewportId: viewportId1,
element: element1,
type: ViewportType.ORTHOGRAPHIC,
defaultOptions: {
orientation: Enums.OrientationAxis.AXIAL,
},
},
{
viewportId: viewportId2,
element: element2,
type: ViewportType.ORTHOGRAPHIC,
defaultOptions: {
orientation: Enums.OrientationAxis.SAGITTAL,
},
},
];
renderingEngine.setViewports(viewportInput);
RenderingEngine will handle creation of the viewports. Next, we need to perform the load on the volume.
Defining a volume is not the same as loading it.
// Set the volume to load
volume.load();
Finally, let the viewports know about the volume.
setVolumesForViewports(
renderingEngine,
[{ volumeId }],
[viewportId1, viewportId2]
);
// Render the image
renderingEngine.renderViewports([viewportId1, viewportId2]);
Final code
const content = document.getElementById('content');
const viewportGrid = document.createElement('div');
viewportGrid.style.display = 'flex';
viewportGrid.style.flexDirection = 'row';
// element for axial view
const element1 = document.createElement('div');
element1.style.width = '500px';
element1.style.height = '500px';
// element for sagittal view
const element2 = document.createElement('div');
element2.style.width = '500px';
element2.style.height = '500px';
viewportGrid.appendChild(element1);
viewportGrid.appendChild(element2);
content.appendChild(viewportGrid);
const renderingEngineId = 'myRenderingEngine';
const renderingEngine = new RenderingEngine(renderingEngineId);
// note we need to add the cornerstoneStreamingImageVolume: to
// use the streaming volume loader
const volumeId = 'cornerStreamingImageVolume: myVolume';
// Define a volume in memory
const volume = await volumeLoader.createAndCacheVolume(volumeId, { imageIds });
const viewportId1 = 'CT_AXIAL';
const viewportId2 = 'CT_SAGITTAL';
const viewportInput = [
{
viewportId: viewportId1,
element: element1,
type: ViewportType.ORTHOGRAPHIC,
defaultOptions: {
orientation: Enums.OrientationAxis.AXIAL,
},
},
{
viewportId: viewportId2,
element: element2,
type: ViewportType.ORTHOGRAPHIC,
defaultOptions: {
orientation: Enums.OrientationAxis.SAGITTAL,
},
},
];
renderingEngine.setViewports(viewportInput);
// Set the volume to load
volume.load();
setVolumesForViewports(
renderingEngine,
[{ volumeId }],
[viewportId1, viewportId2]
);
// Render the image
renderingEngine.renderViewports([viewportId1, viewportId2]);
You should be able to see:
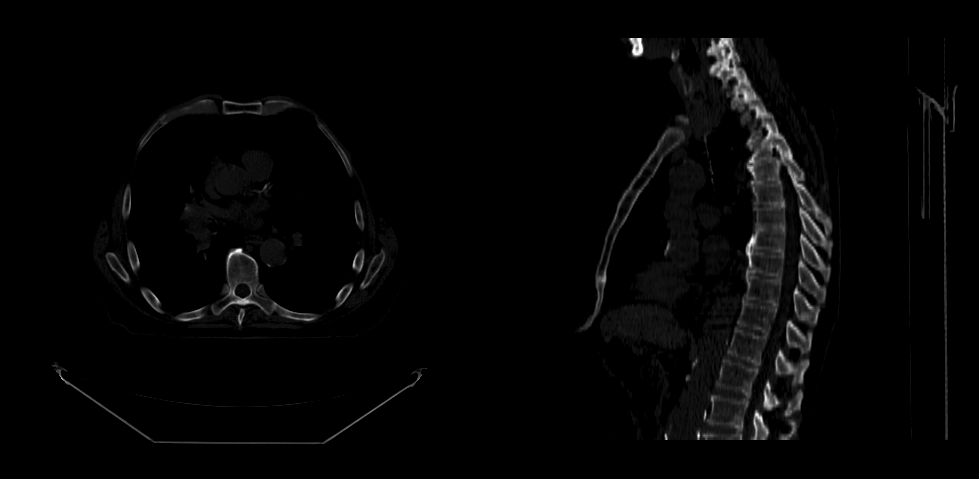
We can apply a window/level callback on the viewports when they load via the setVolumesForViewports API.
setVolumesForViewports(
renderingEngine,
[
{
volumeId,
callback: ({ volumeActor }) => {
// set the windowLevel after the volumeActor is created
volumeActor
.getProperty()
.getRGBTransferFunction(0)
.setMappingRange(-180, 220);
},
},
],
[viewportId1, viewportId2]
);
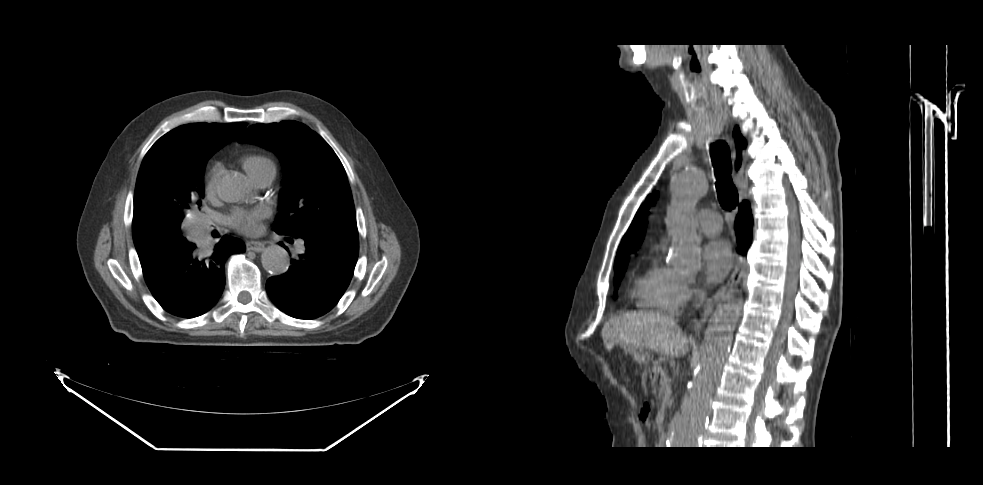
Read more
Learn more about:
For advanced usage of Stack Viewport, please visit VolumeViewport API example page.